Dr Miguel Stanley: "[Ceramic implants] are excellent for patients who are sensitive to metal or are looking for a metal-free alternative"
Terminal dentition can be very painful for patients. The term refers to patients who have lost all or most of their natural teeth. Fortunately, the problem faced by many patients around the world can be solved. And the path to complete functional and aesthetic rehabilitation can be metal-free.
Two-piece implants made of high-performance ceramics are increasingly becoming the focus of clinical application due to their biological and material properties. No metal corrosion, less plaque accumulation and better biological compatibility of zirconia ceramics compared to titanium make ceramic implants a preferred treatment method for patients with metal intolerance.
In this case, Dr Miguel Stanley presents a full arch rehabilitation with implant-supported prosthesis on Zeramex XT implants in a 62-year-old female patient with metal hypersensitivity.
Full-arch rehabilitation with implant-supported prosthesis on 6 Zeramex XT implants: surgical and prosthetic phase
Prior to rehabilitation, a pre-implant rehabilitation of the maxilla was performed. 6 Zeramex XT implants were placed to support the prosthesis. Implant placement was performed according to Zeramex XT surgical protocols. The healing time was approximately 6 months. After successful bone integration, the implants were uncovered. To support the modulation of the gingiva, PMMA was used for the temporary restoration. The fabrication of the custom abutments and the prosthesis was done with CAD/CAM technology. This was followed by the final implant restoration.
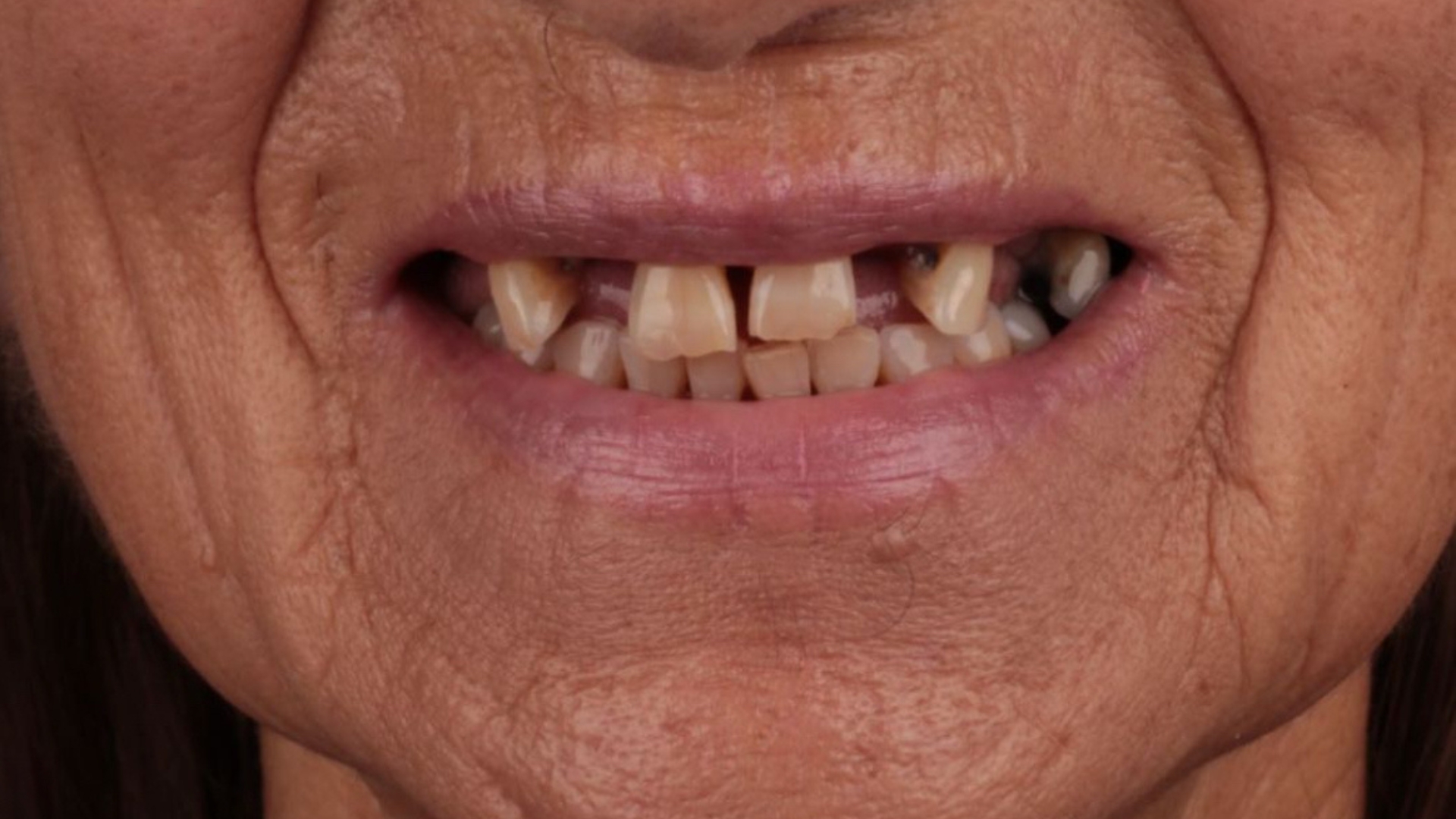
Fig. 1: Terminal dentition
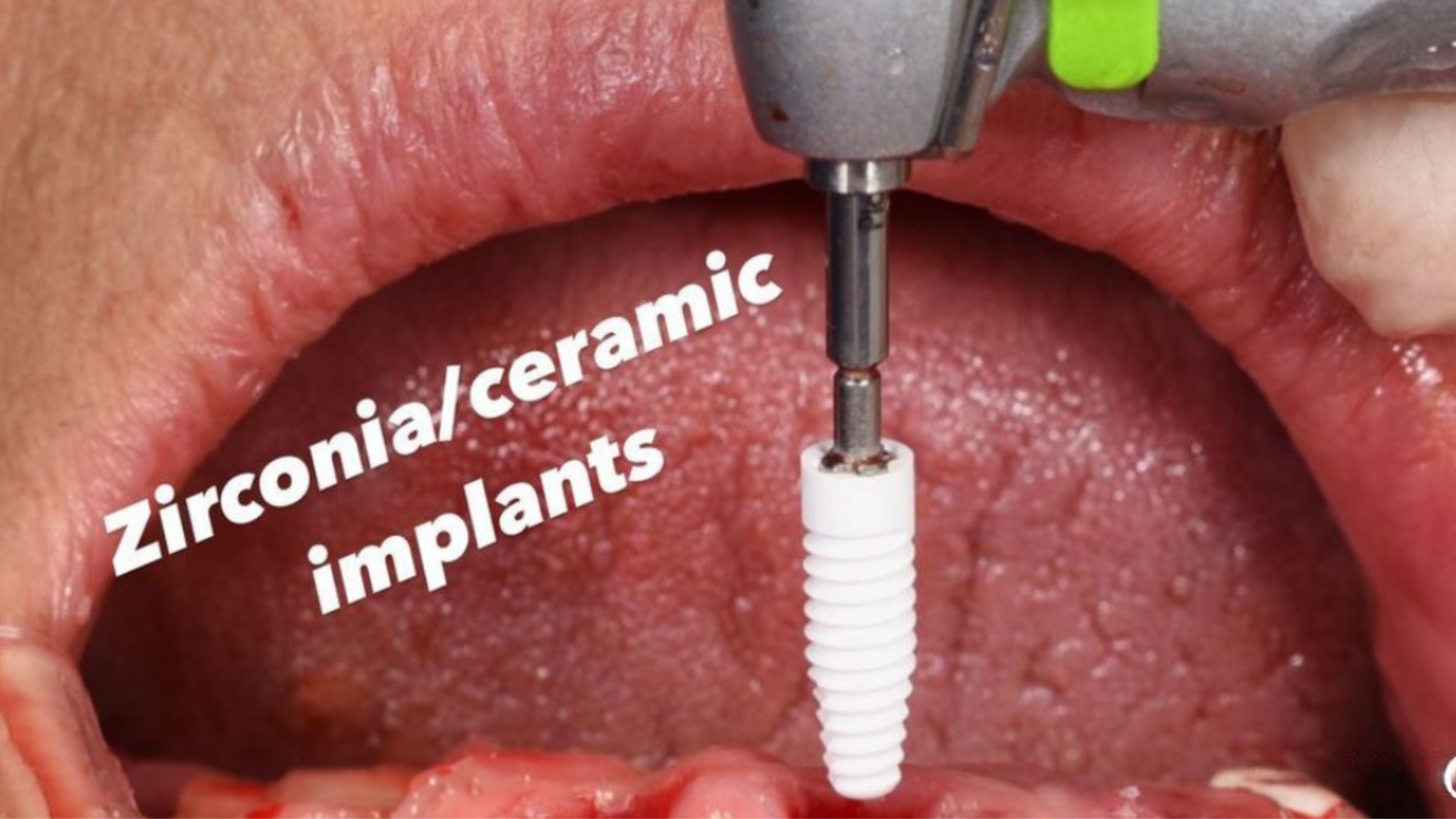
Fig. 2: Implantation
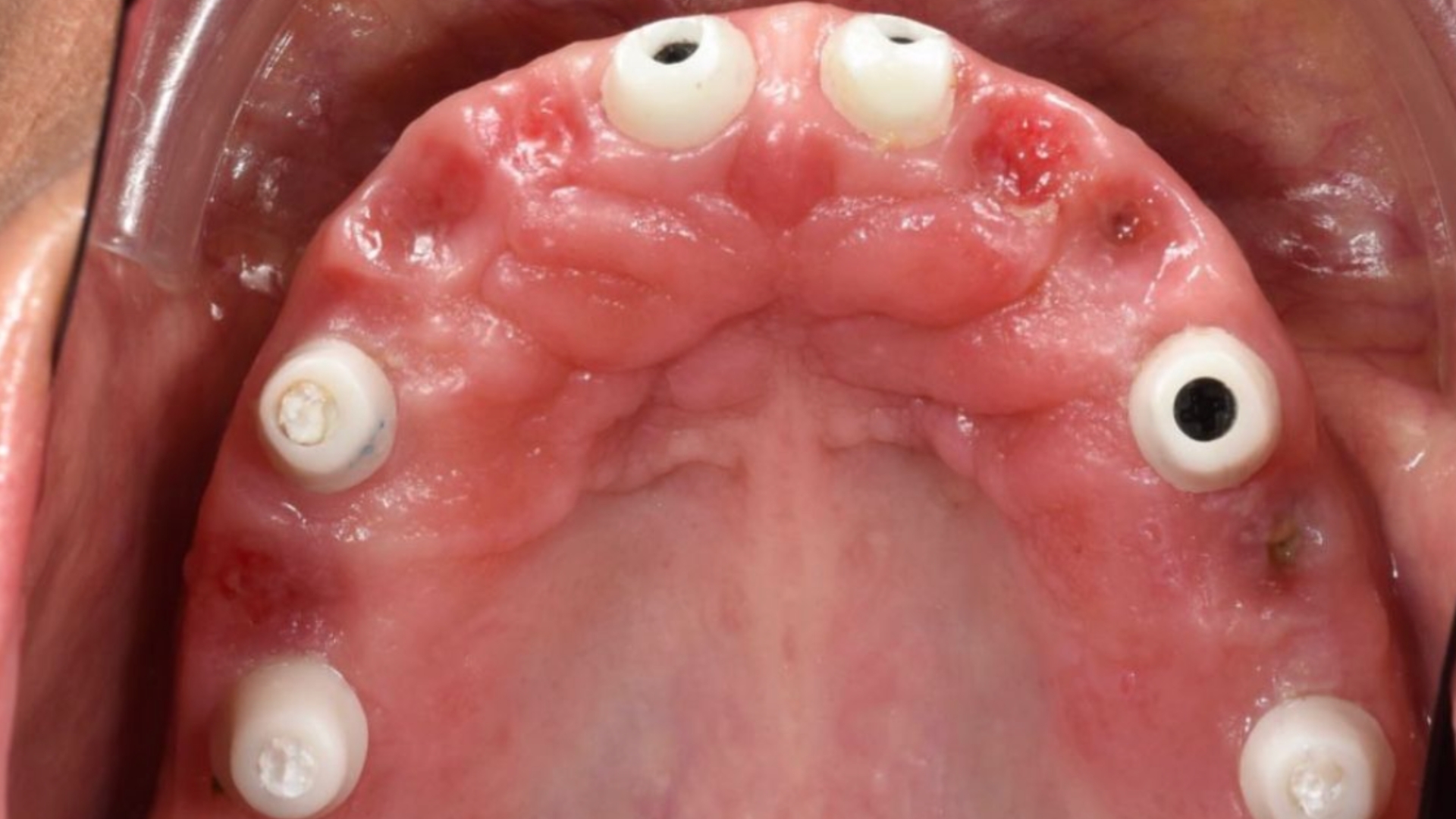
Fig. 3: Abutment for temporary restoration
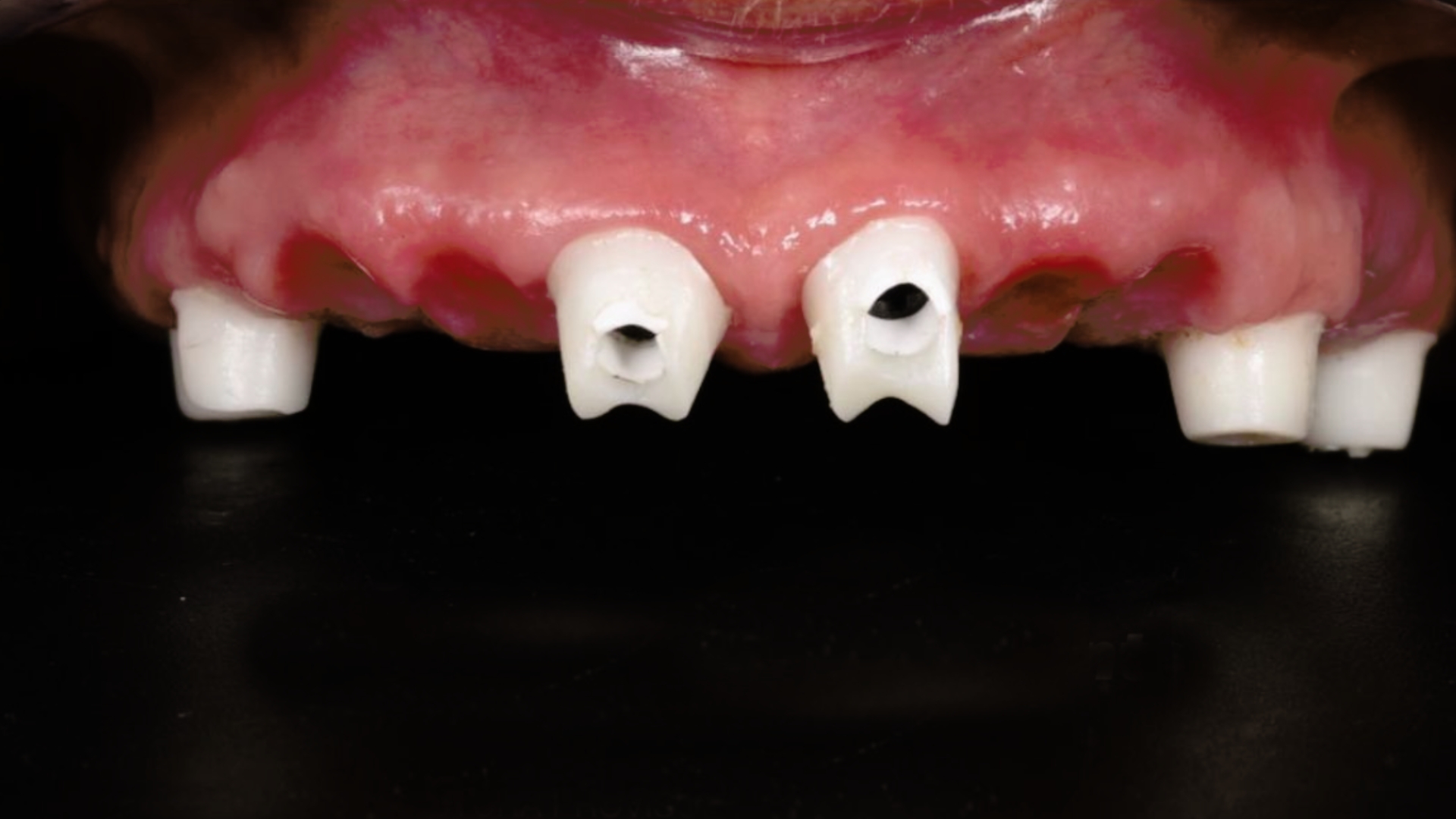
Fig. 4: Customised abutments
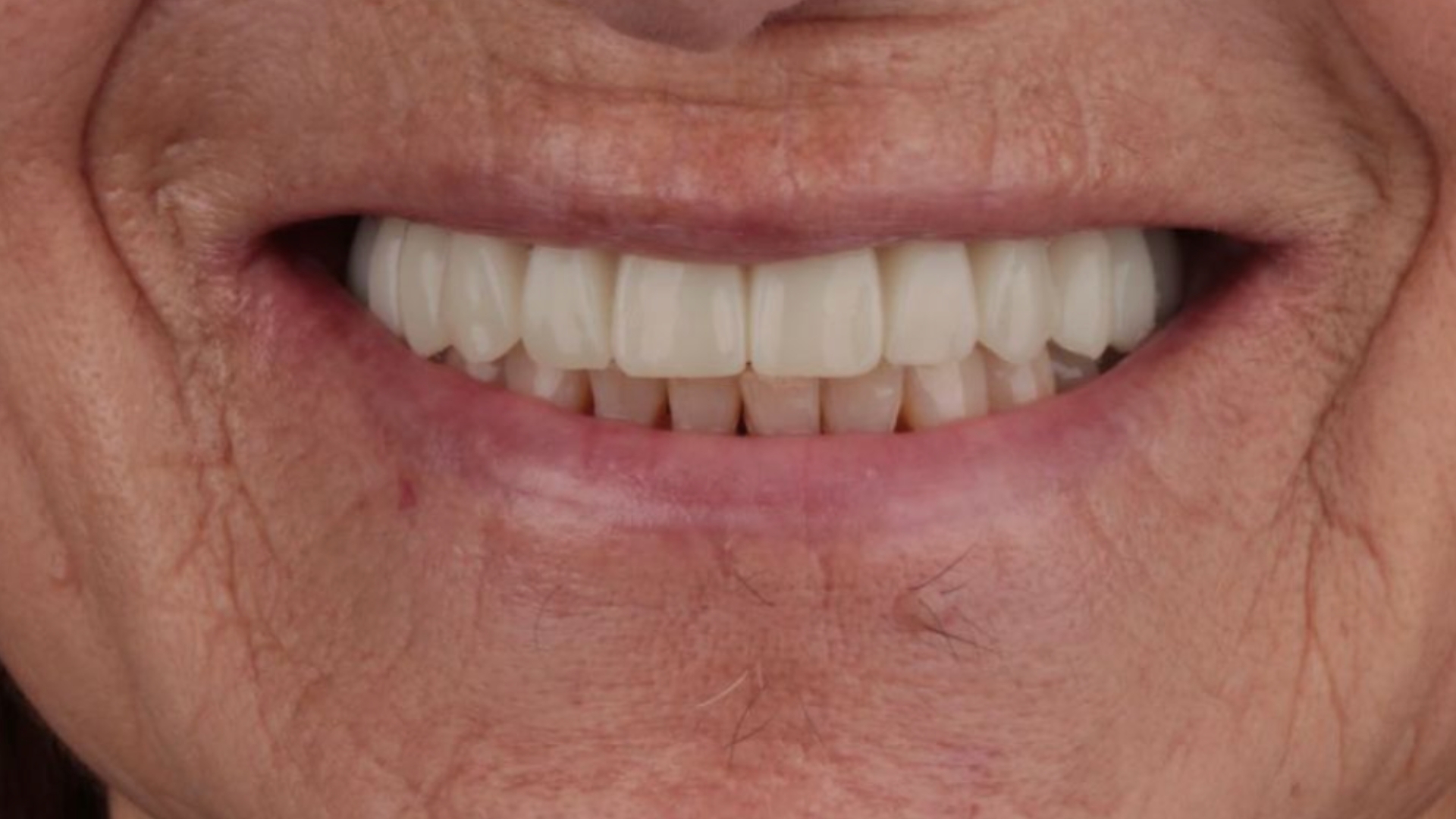
Fig. 5: Temporary restoration PMMA
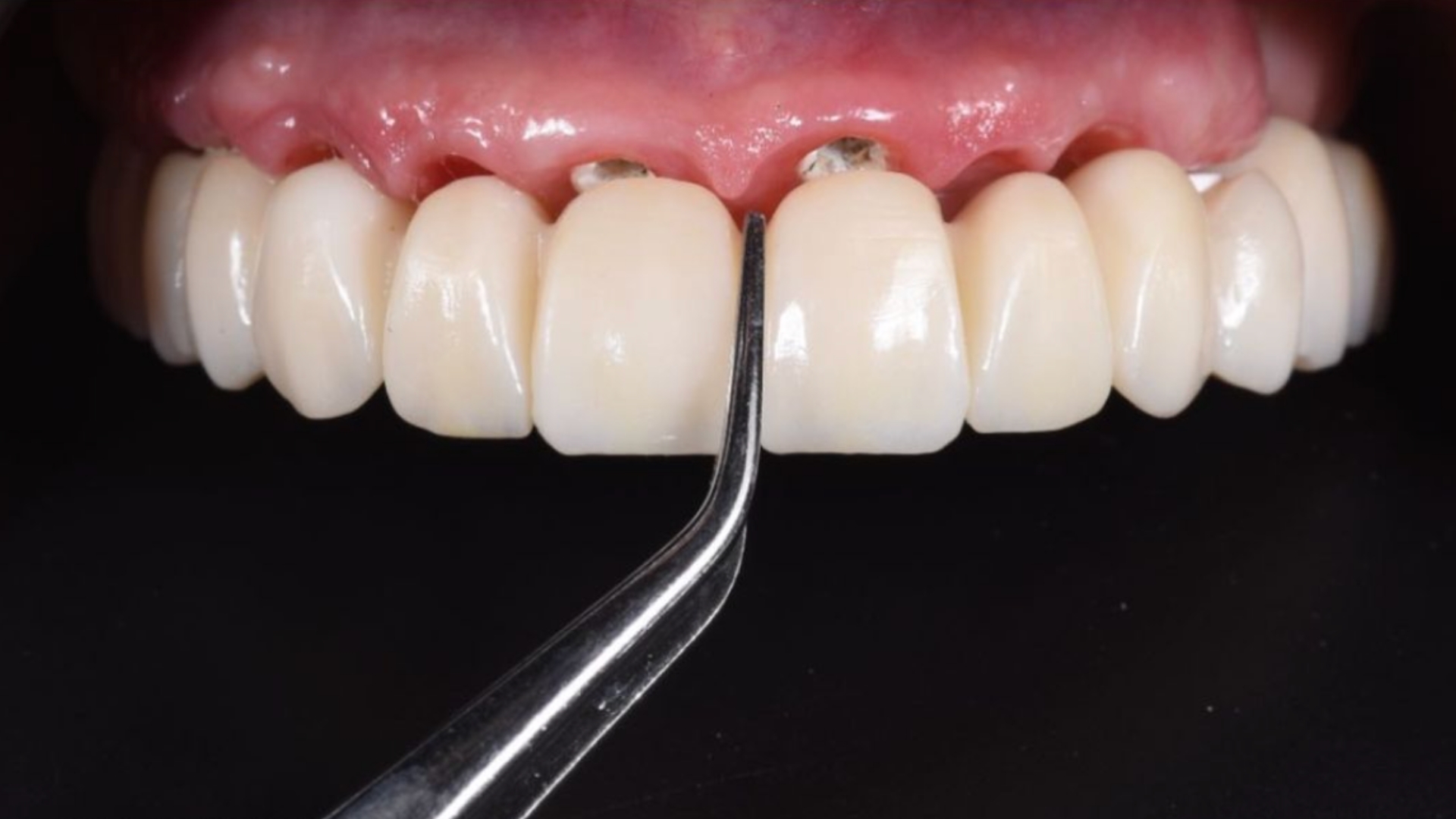
Fig. 6: Implant-supported restoration
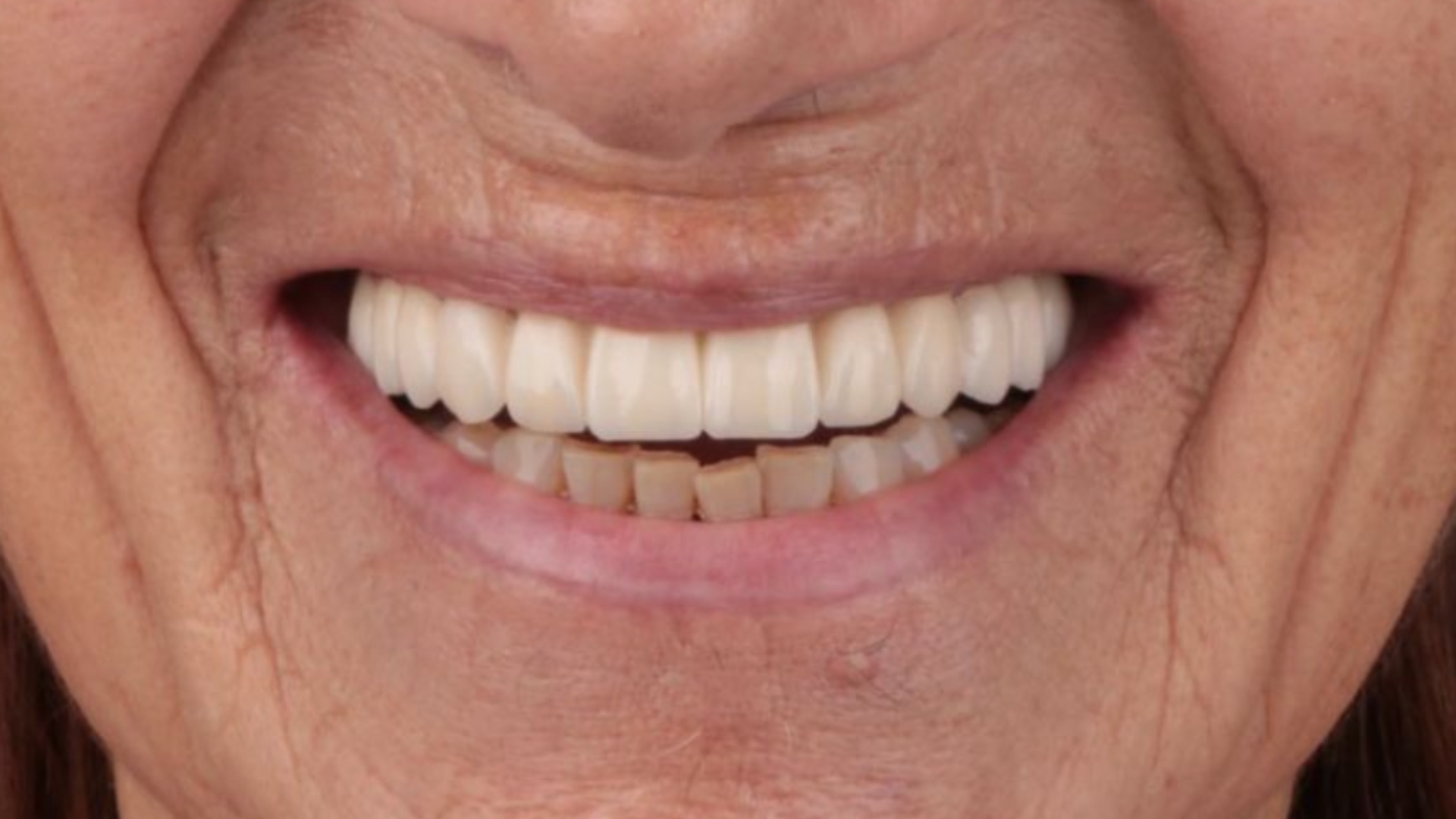
Fig. 7: Result of the restoration
Dr Stanley says: "Ceramic implants are definitely on the rise and are becoming an increasingly popular treatment option for our patients at the White Clinic. They are great for patients who are sensitive to metal or are looking for a metal-free alternative. It is essential to maintain good vitamin D levels and clean the bone very well before insertion. Once inserted, they are easy to rehabilitate. I have to say I love the two-piece nature of the system and the carbon fibre reinforced screw."
S3 Guideline "Material incompatibilities in dental endosseous implants".
The newly published S3 guideline "Material incompatibilities in dental endosseous implants" shows the continuing relevance of the topic. It recommends that dental ceramic implants can be considered as a treatment option if a local titanium-related inflammatory reaction is suspected. However, the cause of an intolerance reaction may also be the metals or impurities present in the superstructures or alloys.
Scientific findings on zirconia implants
For all advantages of titanium as an implant material, the literature shows clear advantages of zirconium dioxide. For example, zirconia implants show less plaque accumulation and less bacterial adhesion (Scarano et al. 2004, Ichikawa et al. 1992). Furthermore, a lower biofilm thickness was observed with zirconia implants (Roehling et al. 2016).
Circular blood flow to the surrounding soft tissue is more similar to that of natural teeth with zirconia ceramics and significantly reduced with titanium (Kajiwara et al. 2015). Better circular blood flow is known to mean healthier gingiva, which results in better outcomes, not only aesthetically (Tartsch 2018).
In the 3- to 5-year results, zirconia implants showed the same "marginal bone loss" as titanium implants (Cionca N, Mombelli A et al. 2016, Spies et al. 2018, Janner et al. 2018). In the study by Roehling et al. (2018), this is even less than with titanium implants. This trend is confirmed by preclinical studies as well as clinical experience (Tartsch 2018).
Peri-implantitis with ceramic implants could not be detected (Cionca N, Mombelli A et al. 2016, Spies et al. 2018, Janner et al. 2018, Roehling et al. 2018).
About Dr. Miguel Stanley
Dr Miguel Stanley is the founder and clinical director of the world-renowned White Clinic. He is co-founder of the Slow Dentistry Global Network and Vice President of the Digital Dentistry Society, as well as a member of many international scientific and academic organisations. Dr Stanley is an Associate Professor at the University of Pennsylvania (USA) and has lectured in more than 50 countries on over 250 topics including advanced implant dentistry, prosthodontics, complex oral surgery, aesthetics, practice management and ethics, as well as his world-renowned "No Half Smiles®" working philosophy. He is one of the first dentists ever to give a TEDx talk and the only one to have hosted a documentary on dentistry for National Geographic. He was recently nominated by his peers as one of the top 100 dentists in the world and by Incisal Edge magazine as one of the "32 most influential people in dentistry".
For more news & updates, please visit our Instagram account.
References
Cionca N, Mombelli A et al.: Pro-inflammatory cytokines at zirconia implants and teeth. A cross-sectional assessment. Clin Oral Investig (2016).
Janner S, Gahlert M, Bosshardt D, Roehling S, Milz S, Higginbottom F, Buser D, Cochran DL: Bone response to functionally loaded, two-piece zirconia implants: A preclinical histometric study. Clin Oral Implants Res 29 (3), 277-289 (2018).
Kajiwara Net al.: Soft tissue biological response to zirconia and metal implant abutments. Implant Dentistry 24 (1), (2015).
Roehling, S.; Schlegel, K.A.; Woelfler, H.; Gahlert, M. Performance and outcome of zirconia dental implants in clinical studies: A meta-analysis. Clin Oral Implants Res 2018, 29 Suppl 16, 135-153.
Roehling S et al.: In vitro biofilm formation on titanium and zirconia implant surfaces. | Periodontol 88 (3), 298-307 (2016).
Roehling S, Gahlert M, Janner S, Bo Meng, Woelfler H, Cochran DL: Ligature-induced peri-implant bone loss around loaded zirconia and titanium implants. International Journal of Oral & Maxillofacial Implants, Review process (2018).
Scarano A, Piattelli M, Caputi S, Favero GA, Piattelli A: Bacterial adhesion on commercially pure titanium and zirconium oxide disks: An in vivo human study. J Periodontol 75, 292-296 (2004).
Spies C, Vach K, Kohal RJ, Hämmerle CHF, Jung RE: Three-year analysis of zirconia implants for single-tooth replacement and three-unit fixed dental prostheses. Clin Oral Implants Res 29 (3), 290-299 (2018).
Tartsch J: Keramikimplantate - Exoten oder sinnvolle Erweiterung des Behandlungsspektrums. ZMK 34-11 (2018).
Tartsch J: Komplexe Restauration mit Keramikimplantaten: zweiteilig, metallfrei und verschraubt. Dentale Implatologie und Parodontologie
(2021).

